-
Vmware Vcenter Converter Could Not Generate Key카테고리 없음 2020. 9. 18. 06:02
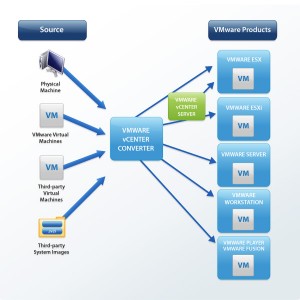
Oh, if you don't want to boot the machine but want to do it remotely, then you can certainly use VMware Converter. I am running 4.0.0, and for destination I have the choice of a vmware infrastructure machine, and vmware workstation or other vmware machine, or a virtual appliance.
Vmware Vcenter Converter Could Not Generate Key File
VMware vCenter Converter Standalone 5.5 | 22 October 2013 | Build 1362012
Last Document Update: 6 January 2014
Check periodically for additions and updates to these release notes.
What's in the Release Notes
These release notes cover the following topics:Introduction to Converter Standalone
VMware vCenter Converter Standalone provides an easy-to-use solution to automate the process of creating VMware virtual machines from physical machines (running Windows and Linux), other virtual machine formats, and third-party image formats. Through an intuitive wizard-driven interface and a centralized management console, Converter Standalone can quickly and reliably convert multiple local and remote physical machines without any disruptions or downtime.
Benefits
- Convert physical machines running Windows or Linux operating systems to VMware virtual machines quickly and without any disruption or downtime.
- Convert third-party image or virtual machine formats such as Parallels Desktop, Symantec Backup Exec System Recovery, Norton Ghost, Acronis, StorageCraft, Microsoft Virtual Server or Virtual PC, and Microsoft Hyper-V Server virtual machines to VMware virtual machines.
- Enable centralized management of remote conversions of multiple physical servers or virtual machines simultaneously.
- Ensure conversion reliability through quiesced snapshots of the guest operating system on the source machine before data migration.
- Enable non-disruptive conversions through hot cloning, with no source server downtime or reboot.
What's New
The VMware vCenter Converter Standalone 5.5 includes the following new functionality:
- Support for virtual machine hardware version 10 (62TB disks, virtual SATA controllers, etc.)
- Support for RedHat KVM virtual machines as a source
- A new option for selecting the network adapter for the target virtual machine
- Support for additional guest operating systems
- Parallel disk conversions
- Virtual SAN support
Installation Notes
You can download, install, and run VMware vCenter Converter Standalone in English only.
Users with limited rights cannot install Converter Standalone 5.5 on Windows. You must log in as an administrator to install Converter Standalone.
Platforms
You can install VMware Converter Standalone 5.5 on the following platforms:
- Windows XP Professional SP3(32-bit and 64-bit)
- Windows Server 2003 R2 SP2 (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Windows Vista SP2(32-bit and 64-bit)
- Windows Server 2008 SP2 (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Windows Server 2008 R2 (64-bit)
- Windows 7 (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Windows 8 (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Windows Server 2012 (64-bit)
Interoperability
Converter Standalone 5.5 supports the following sources.
- Physical machine running an operating system noted in Supported Guest Operating Systems
- VMware Desktop products
- Workstation 7.x, 8.x, 9.x, and 10.x
- Fusion 3.x, 4.x, 5.x, and 6.x
- Player 3.x, 4.x, 5.x, and 6.x
- VMware vCenter virtual machines
- vSphere 5.5
- vSphere 5.1
- vSphere 5.0
- vSphere 4.1
- vSphere 4.0
- Third-party backup images and virtual machines
- Acronis True Image Echo 9.1 and 9.5, and Acronis True Image Home 10 and 11 (.tib)
- Symantec Backup Exec System Recovery (formerly LiveState Recovery) 6.5, 7.0, 8.0, and 8.5, and LiveState Recovery 3.0 and 6.0 (.sv2i format only)
- Norton Ghost version 10.0, 12.0, and 14.0 (.sv2i format only)
- Parallels Desktop 2.5, 3.0, and 4.0 (.pvs and .hdd). Compressed disks are not supported
- Parallels Workstation 2.x (.pvs). Compressed disks are not supported. Parallels Virtuozzo Containers are not supported.
- StorageCraft ShadowProtect Desktop, ShadowProtect Server, ShadowProtect Small Business Server (SBS), ShadowProtect IT Edition, versions 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.1, and 3.2 (.spf)
- The Microsoft VHD format for the following sources:
- Microsoft Virtual PC 2004 and Microsoft Virtual PC 2007 (.vmc)
- Microsoft Virtual Server 2005 and 2005 R2 (.vmc)
Depending on the selected source, you can convert it to the following destinations.
- VMware vCenter virtual machines
- ESX 4.0 and 4.1
- ESXi 4.0, 4.1, 5.0, 5.1, and 5.5
- vCenter Server 4.0, 4.1, 5.0, 5.1, and 5.5
- VMware Desktop virtual machines
- VMware Workstation 7.x, 8.x, 9.x, and 10.x
- VMware Player 3.x, 4.x, 5.x, and 6.x
- VMware Fusion 3.x, 4.x, 5.x, and 6.x
Earlier releases of Converter Standalone (versions 3.x and 4.x) might not be compatible with VMware vSphere 5.x.
Supported Guest Operating Systems
Converter Standalone 5.5 supports the following guest operating systems:
- Windows XP Professional SP3 (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Windows Server 2003 R2 SP2 (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Windows Vista SP2 (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Windows Server 2008 SP2 (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Windows Server 2008 R2 (64-bit)
- Windows 7 (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Windows 8 (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Windows Server 2012 (64-bit)
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 3.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 9.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Ubuntu 10.04 LTS (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Ubuntu 12.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Ubuntu 13.04 (32-bit and 64-bit)
CAUTION: During cloning of powered on Linux machines, Converter Standalone 5.5 preserves the following source file systems on the destination: ext2, ext3, ext4, reiserfs, and vfat. All other source file systems are converted into ext3 file systems on the destination virtual machine.
For more information about the operating systems supported by Converter Standalone and other system requirements, see the
VMware vCenter Converter Standalone User's Guide.
Prior Releases of Converter Standalone
Features from prior releases of Converter Standalone are described in the release notes for each release. To view release notes for prior releases of Converter Standalone, click one of the following links:
Known Issues
The Converter Standalone 5.5 release contains the following known issues:
Installation
If the name of the Converter Standalone installation directory contains non-ASCII characters, you might experience conversion and configuration problems
If the name of the Converter Standalone installation directory contains non-ASCII characters, the following issues might occur:- Conversion and configuration of Windows virtual machines might fail with an error message
Unable to reconfigure destination virtual machine. In thevmware-converter-worker.log, this error generates a message similar toError 3 (error restoring key: Unknown error 3 (0x3) (3)) restoring registry key C:しã™ãŸã•かãn°..dataSKUNKWORKS_FILLER into... - If you try to convert a Linux physical machine, you might receive an error message in the Convert Machine wizard
Unable to obtain hardware information.
You must restart machines that run 64-bit Windows Vista or later before re-installing Converter Standalone
If you uninstall Converter Standalone from a 64-bit Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, or Windows 7 machine and do not restart it, a subsequent Converter Standalone installation might fail with the following error message:Error 29144. Could not install service Vstor2 MntApi 1.0 Driver (shared). Please reboot and try to install again.
Workaround: Restart the Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, or Windows 7 machine and try installing Converter Standalone again.Converter Standalone installer removes Workstation 6.5.x remote agents without notification
When you use Workstation 6.5.x to hot-clone a Windows source machine, Workstation deploys a remote Workstation agent on the source. If you choose to leave the remote agent on that source and then install Converter Standalone on the same machine, the Converter Standalone installer uninstalls that agent without any warning messages.Users with limited rights cannot install Converter Standalone on Windows
If you are logged in to Windows as a non-administrator user, the following error message is displayed while the InstallShield is extracting files for Converter Standalone installation:Unable to save file:
C:WINDOWSInstaller
The system cannot find the path specified.
The error is displayed because limited users do not have the required write permissions.
Workaround: Select the%TEMP%directory to extract the installation files:- Click OK in the error message. A Save As dialog box appears.
- Browse to the Temp folder of the current user (for example,
C:Documents and Settings'username'Local SettingsTemp) and click OK.
NOTE: You still need to log in as an administrator to install Converter Standalone.
You cannot install vCenter Converter 4.2.1 on the same machine where you have already installed Converter Standalone 5.5
If you install Converter Standalone 5.5 and then install vCenter Converter 4.2.1 server on the same machine, downloading the vCenter Converter 4.2.1 plug-in from vSphere Client fails.
Workaround: First install vCenter Converter 4.2.1 and then install Converter Standalone 5.5.General
If you try to convert a source physical or virtual machine to a managed destination by using thick provisioned disks with large empty spaces on them, the conversion task might fail
If you try to perform a disk-based cloning of a physical or virtual machine to a managed destination by using thick provisioned disks with large empty spaces on them, the conversion task might fail with an error messageUnable to clone disk source_disk on the virtual machine virtual_machine_name. The following messages appear in the log file:[03200 warning 'Default'] [,0] [NFC ERROR] NfcNetTcpRead: bRead: -1
[03200 warning 'Default'] [,0] [NFC ERROR] NfcNet_Recv: requested 264, recevied only 0 bytes
[03200 warning 'Default'] [,0] [NFC ERROR] NfcFile_Stream: Failed to get message from source
[03200 warning 'Default'] [,0] [NFC ERROR] NFC_NETWORK_ERRORThe destination ESX server must return an acknowledgement after each processed NFC write request. If the source sends a large block of zeroes that must be written it might take a long time for the ESX to return the acknowledgement. Thus, the Converter assumes that the operation has timed out and closes the connection, no matter that the ESX server is still writing to the target disk.
Workaround: Change the destination disk type to thin.
Converting Linux physical machines fails if the size of a destination disk is 2 TB or larger
If you try to convert a Linux physical machine, the conversion job fails at 2% with an error messageCalculateGPTPartitionLocations failed, if a destination disk is 2TB or larger.Workaround: In the most cases, you can resolve this issue by decreasing the size of the destination disk to less than 2 TB by shrinking the destination volume or splitting the volumes across several destination disks.
When converting hosted virtual machines with unpartitioned disks, you might not be able to obtain hardware information about the source
When converting hosted virtual machines with unpartitioned disks, you might not be able to obtain hardware information about the source. In such case, the following error messages might appear in the worker log:[01628 warning 'Default'] Partition:Invalid sector magic number.[01628 warning 'Default'] ERROR: Failure during open: Reading disk signature[01628 error 'Default'] [BaseDiskSetComputer::DoOpen] OpenDisks failed, mntapi error: 32.
Workaround: Remove the unpartitioned disks from the conversion job.
A running P2V conversion job fails if you create a new conversion job for the same Windows source machine and use a different port to deploy the Converter Standalone agent
If, while running a P2V conversion job, you start creating another conversion job for the same powered on Windows source machine, and specify a port for the connection, Converter Standalone deploys the Converter Standalone agent using the port you specified. If the connection port is different from the one that is being used for the already running conversion job, both jobs fail. The following error message appears in the Job summary tab for the first conversion job:FAILED: A general system error occurred: No connection could be made because the target machine actively refused it. The following error message appears in the Job summary tab for the second conversion job:FAILED: Unable to create a VSS snapshot of the source volume(s). Error code: 2147754774 (0x80042316).You cannot copy running conversion or configuration jobs
If you open the Copy As New wizard for a running configuration or conversion job when the source is a virtual machine or a backup image and you click Next, the wizard displays the error messageUnable to obtain hardware information for the selected machine.
Workaround: Wait for the job to complete before selecting Copy as New in its pop-up menu.Linked Cloning of source images greater than 2GB to a network share that does not support large files fails
Creating linked clones from source images that are larger than 2GB to a network share that does not support large files (for example, to a Linux SMB share) fails. Converter Standalone does not split the source files into smaller chunks. If the source is larger than the supported file size on the destination, the conversion tasks fails.Creating a conversion job to convert a standalone VMware source with a VMDK file greater than 2GB from a network share that does not support large files, fails
If you select a standalone virtual machine source with VMDK file greater than 2GB residing on a remote network location that does not support large files (for example, Linux SMB share), the following error message appears in the Converter wizard on clicking Next or View source details:Unable to obtain hardware information for the selected machine.
Workaround: Map the network shared folder to the machine where Converter Standalone runs, and select the source from there.Converter Standalone cannot detect the power state of VMware Workstation or other VMware hosted source virtual machines if they are located on a read-only network share
If the source machine is a Workstation or another VMware hosted source and is located on a network share with read-only permissions, Converter Standalone cannot detect if the source is powered on or suspended. This might lead to data inconsistency on the destination machine if changes are made to the powered on source virtual machine during conversion.
Workarounds:- Verify that the source virtual machine is powered off prior to conversion.
- Provide write privileges to the network share where the source virtual machine resides.
Conversion jobs from and to ESX hosts that are not connected to vCenter Servers fail if the number of disks on the source machine is more than nine
When converting a source machine that has more than nine disks, conversion fails with the following error in the log file:Error on logout (ignored): Operation timed out.
SSLStreamImpl::BIORead (3BBA4E8) timed out
The error is due to the limited number of NFC connections that can be established to ESX hosts that are not connected to vCenter Server instances.
Workaround: Connect to the destination ESX host through a vCenter Server. In this case, the number of source disks is limited to 27 for ESX and to 23 for ESXi hosts.Converting source volumes with unrecognized file systems might prevent the destination virtual machines from starting
While you are setting up a volume-based cloning task in one of the Converter Standalone wizards, the volume name might be missing in some rows of the Source Volumes tab. This means that Converter Standalone does not recognize the file system on those volumes. The destination virtual machine that is created as a result of such a conversion task might fail to start up. Nevertheless, Converter Standalone copies the source volume data to the destination using block-level copying.
Workaround: configure the destination virtual machine after the conversion.Converting standalone VMware sources with a VMDK file greater than 2GB to a hosted destination that resides on a network share that does not support large files, fails
If you select a standalone virtual machine source with VMDK file greater than 2GB and try to convert it to hosted destination residing on a remote network location that does not support large files (for example, Linux SMB or NFS share), the conversion job might fail with one of following error messages:Unable to connect to the virtual diskRemote server closed connection after 0 response bytes readAn error occurred during an operation on a virtual disk
Internal Inconsistency errors
Workaround:- In the main application window of Converter Standalone, right-click the failed job and select Copy As New..
- Go to the Options page and select Data to Copy.
- In the Data to Copy pane, select the volumes to copy and click Advanced.
- On the Destination layout tab, select Split not pre-allocated or Split pre-allocated as the destination disk type.
- Click Next to view a summary of the conversion job.
- On the Ready to Complete page, click Finish to resubmit the job.
Converter Standalone is unable to detect the system volume if it resides on a SCSI disk and IDE disks are present in the source machine
On source machines with SCSI and IDE disks, Converter is unable to detect the system volume if the system volume resides on a SCSI disk. Converter only checks the first IDE disk in such configurations.If the hardware configuration of the source machine is modified while the Conversion wizard is open, you need to restart the conversion wizard if you want to view correct source details
Source machine details are retrieved per wizard session, as this is a time-consuming process. If some changes occur on the source machine (such as adding memory or hard drives) after this information is retrieved, the Conversion wizard does not show information about the changes.
Workaround: Restart the conversion wizard.Cloning a source that contains file system errors might result in a damaged virtual machine
See Cloning a source that contains file system errors may result in a damaged copy (KB 1006689).Timeout on SSL handshake when converting over a WAN link
Converter Standalone does not support conversion over a WAN. When trying to perform a conversion over a WAN link, you might experience an SSL timeout because the timeout for SSL handshakes is two minutes.
Workaround:- To avoid the two-minute handshake, perform a conversion to a hosted destination machine (for example, Workstation) in the same LAN.
- Copy the temporary virtual machine and send it over the WAN to the remote site.
If the intended destination is a Workstation virtual machine, this completes the process. - If the intended destination is ESX, import the Workstation virtual machine to the ESX server.
User Account Control (UAC) prevents installing Converter Standalone agent if you are not using the default Administrator account to connect to a powered on source machine
If you are setting up a task to convert a powered on source machine that runs Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows Server 2012, or Windows 8 and you use a non-default Administrator account to log in to the source machine, the following error message might appear when you try to install Converter Standalone agent on the source machine:Insufficient permissions to connect to xxxxxxx. Herexxxxxxxis the IP address of the source machine. This is because Converter Standalone server cannot install Converter Standalone agent when UAC is enabled and you are logged in to the source as non-default Administrator user.
Workaround: Disable the UAC on the source machine before you start the Conversion wizard. You can search the Microsoft Web site for procedures on disabling the UAC depending on the source operating system. For Windows Server 2012 and Windows 8, in addition to disabling UAC, you must perform the following steps:- In the Windows Start menu, type
gpedit.msc. The Local Group Policy Editor opens. - Navigate to Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options.
- Disable the Run all administrators in Admin Approval Mode setting.
- Restart.
The Reconfigure Virtual Machine wizard does not display correctly the vDS port group name
When you reconfigure a virtual machine that uses dvSwitch and you navigate to the Network interface settings pane, the Network name text box does not display the name of the dvSwitch after the port group name. Onlyport groupis displayed instead.The reported network transfer rate might not be correct
The reported network transfer rate might be higher than the actual one because of the inherent compression used by the network protocol. This does not affect the network throttling.Adding a virtual machine to a domain might fail if you specify a fully qualified user name
DOMAIN_NAME/USER_NAME
When configuring a virtual machine, you might not be able to add the virtual machine to a domain if you use a fully qualified user name ().
Workaround: Specify the user name without including the domain name.Conversion of a physical machine running Microsoft Windows XP or Windows Server 2003 with a BCD manager (Boot Manager for Windows Vista) and later might fail
If you try to convert a physical machine with a BCD manager, the P2V conversion might fail in the following cases:- Microsoft Windows Vista or later is installed on the source physical machine, which is a dual-boot machine currently running Microsoft Windows XP or Windows Server 2003.
- Microsoft Windows Vista or later is installed as a second operating system on the source physical machine and later is removed, but the BCD manager is left on the source machine.
- Boot the later version of Windows (Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, or Windows 7).
- Perform a physical source conversion.
- On the newly created virtual machine, boot a repair CD for the earlier version of Windows (Windows XP or Windows Server 2003).
- Remove the BCD manager and revert the operating system to its compatible boot process.
- Shut down the virtual machine and reconfigure it by using the Converter Standalone configuration wizard. Now you can boot the machine.
- On the source machine, boot a repair CD of the corresponding operating system.
- Remove the BCD manager and revert the operating system to its compatible boot process.
The specified parameter was not correct:'info.owner'message
If Converter Standalone is installed in a client-server mode and you have connected by using a username, which is the same as the computer name, submitting a job might fail withThe specified parameter was not correct:'info.owner'message.
Workaround: Connect by using a different user account with administrative rights.
You might not be able to convert more than nine disks at once
On ESX 3.5 and 4.0, conversion might fail if you try to convert more than nine disks.
Workaround: Perform conversion in multiple steps to convert the disks in portions of up to nine. Then, attach all the disks to the target machine.
Windows Sources
You can perform only volume-based cloning on the block level for ReFS-formatted volumes
Converter Standalone lets you perform cloning of ReFS-formatted volumes with the following limitations:- You can perform only volume-based cloning on the block level.
- You cannot use ReFS-formatted volumes in incremental updates.
- You cannot shrink or expand ReFS-formatted volumes.
Configuration of Windows virtual machines with multiple active partitions might not complete
For Windows virtual machines with multiple active partitions, Converter Standalone might not recognize the boot partition and might not be able to complete the reconfiguration of the destination virtual machine. In such cases, after the conversion job is 96-98% complete, the conversion job status changes to Failed and an error message appears. For example:FAILED: Unable to find the system volume, reconfiguration is not possible.In the Worker/Agent log this issue is identified by the following statement:[#### warning 'Default'] ERROR: [Mntapi_GetFirstBootDisk] more that *one* active volume found. Current active disk #0, another active disk #1.
Workaround 1: Mark all non-boot active partitions on the destination machine as inactive and run configuration on the destination machine.- Boot into Windows Recovery Console on the destination machine.
- Run diskpart.exe.
The diskpart command prompt appears. - (Optional) To list the available disks, enter
list disk. - Enter
select disk <disk_number>. - (Optional) To list the partitions on the selected disk, enter
list partition. - Enter
select partition <partition_number>. - Enter
inactive. - Repeat steps 4-7 to mark another partition as inactive.
- Power off the destination machine.
- Run Converter Standalone and configure the destination machine.
Workaround 2: Mark all non-boot active partitions on the source machine as inactive and attempt to run the conversion again.
- On the source machine, run diskpart.exe.
The diskpart command prompt appears. - (Optional) To list the available disks, enter
list disk. - Enter
select disk <disk_number>. - (Optional) To list the partitions on the selected disk, enter
list partition. - Enter
select partition <partition_number>. - Enter
inactive. - Repeat steps 2-6 to mark another partition as inactive.
- Run Converter Standalone and start the conversion again.
Conversion of a local powered on source machine fails at 1%
If you select This local machine as a conversion source and a Converter Standalone agent from a previous Converter Standalone version is installed on the source machine, the conversion task fails at 1%. The following error message appears in the Status line of the Task progress tab:FAILED: Unable to create a VSS snapshot of the source volume(s). Error code: 127 (0x0000007F).
This is because the Converter Standalone installer cannot upgrade previous versions of Converter Standalone agents.
Workaround: Manually uninstall Converter Standalone agent from the source machine and create a new conversion task.Converter Standalone worker process stops responding if you try to copy a configuration job during guest operating system customization
If you right-click a running configuration job and select Copy As New while the destination machine is being customized, Converter Standalone worker process stops responding.
Workaround: Wait for the configuration job to complete before you copy it.Subsequent P2V conversions of remote source machines that run 64-bit Windows Vista or later might fail after a successful conversion
If you convert successfully a remote source machine that runs 64-bit Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, or Windows 7 operating system and then try converting it again, the conversion fails with the error messageConverter Standalone Agent installation failed on x.x.x.x Error code: 1603, where x.x.x.x is the IP address of the source machine.
This error message might occur if automatic uninstall of remote Converter Standalone agent has been enabled during the first successful conversion.
Workaround: Restart the remote source machine and try running the conversion task again.Converter Standalone does not preserve disabled network adapters during conversion of physical machine sources that run on Windows
During P2V conversion of Windows source machines, Converter Standalone does not detect disabled network adapters on the source and does not preserve them on the destination virtual machine.
Workaround: On the Options page of the Converter Standalone wizard, click Networks to add network adapters to the destination virtual machine.Microsoft Windows Vista reboots repeatedly after customization
Providing wrong customization information might cause the destination virtual machine to reboot repeatedly if the source operating system is Microsoft Windows Vista. During conversion or configuration, if you choose to customize Microsoft Windows Vista and provide wrong customization information, for example an invalid serial key, the customized destination reboots repeatedly. This is a known issue with Microsoft Windows Vista.
Workaround: Make sure that the provided customization information is valid.Converter Standalone does not support cloning powered on Windows Server 2008 sources with FAT/FAT32 volume file system
VSS under Windows Server 2008 does not support FAT/FAT32. Trying to convert a FAT/FAT32 volume causes the conversion task to fail.
Workaround: Deselect all FAT/FAT32 volumes on the Options page of the Conversion wizard.Converter Standalone remote agent does not notify the user about Converter 3.0.x or 4.0.x remote agents that have been installed on the source system during remote hot cloning process
If Converter Standalone is converting a remote machine source that already has a remote agent from Converter version 3.0.x or 4.0.x, it uninstalls the old remote agent without issuing a notification or warning message. This prevents older Converter versions from converting this source machine later.Previous Converter versions cannot convert source machines that have Converter Standalone 5.5 agent installed on them
Converter Standalone 5.5 agent is deployed on the source machine during conversion. If Converter Standalone 5.5 agent is not uninstalled after the conversion, older Converter versions cannot deploy their agents on top of the newer Converter Standalone agent version. Therefore, you cannot use previous Converter versions to convert sources that have already been converted with Converter Standalone 5.5.
Workaround: Uninstall Converter Standalone 5.5 agent before trying to convert the source with an older Converter version.Stopping Converter Standalone processes during file-level cloning might cause the machine that runs the Converter Standalone server service to restart
During file-level cloning of source systems that run Windows XP or Windows Server 2003, if any of the following Converter Standalone process is forcibly stopped, the machine on which the stopped process was running might automatically reboot.- VMware Converter Standalone Integrated Worker
- VMware Converter Standalone Integrated Agent
Workaround: Do not stop any Converter Standalone services on the source machine during file-level cloning. For more information and hot fix, check the Microsoft site Error message when a Delayed Write Failure event is reported in Windows Server 2003: 'Stop 0x00000019 - BAD_POOL_HEADER' or 'Stop 0xCD PAGE_FAULT_BEYOND_END_OF_ALLOCATION'.Converter Standalone does not change PIC HAL to APIC HAL during conversion of Windows source machines
If the source to convert is running a Programmable Interrupt Controller (PIC) HAL, Converter Standalone does not change the PIC HAL to an Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC) HAL in the destination virtual machine. As a result, the destination virtual machine might not boot or might fail to perform as expected. To find out which HAL is running, go to Windows Device Manager and select Computer in the list of devices. If it displays Standard PC or Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) PC, you are running a PIC HAL.
Workaround: VMware virtual machines are APIC computers. If your source computer is a PIC computer that runs a PIC HAL, you must update the HAL in the destination virtual machine to APIC HAL after the conversion. For more information on configuring the correct HAL, check the Microsoft Web site HAL options after Windows XP or Windows Server 2003 Setup.
Note: Microsoft does not support running a PIC HAL on an APIC computer. If your source is an APIC computer running a PIC HAL, you must configure the correct HAL on the source machine before starting the conversion.Owner name and organization are not displayed properly after customizing the guest operating system
sysprep.inf
After customizing the guest operating system, Unicode characters used for owner name and organization on the Computer Information page do not appear the way they were set in the Conversion or the Configuration wizard.
For all Windows operating systems except Windows Vista, customization parameters such as user name and organization must use characters only from the local encoding of the default user profile of the guest. For example, you can use Japanese characters for the user name only on a guest whose default user profile's local encoding is set to Japanese. These restrictions do not apply to Windows Vista guests because Windows Vista uses a UTF-8 encoded XML file to store the Microsoft sysprep parameters. Earlier versions of Windows use thefile, and the Microsoft Windows mini-setup process reads that file in the local encoding only.
Workaround: Either avoid Unicode characters when assigning owner name and organization name for the destination virtual machine, or use the workaround described at: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/310441/.Converter can convert FAT/FAT32 volumes during hot cloning only if the source machine has at least one NTFS volume
For source machines running under Windows versions earlier than Windows Server 2008, VSS can take snapshots of FAT/FAT32 volumes only if the source machine has at least one NTFS volume. For all operating systems that support volume-based cloning, you need at least one NTFS volume for VSS to work.Converter Standalone agent does not start automatically after reboot
If the source machine starts up too slowly, Converter Standalone agent might not start automatically after the source machine is restarted.
Workaround: Start the Converter Standalone agent manually:- Right-click My Computer and select Manage.
- In the Computer Management window, select Services and Applications >Services on the left.
- In the list on the right, double-click VMware Converter Standalone Agent.
- Click Start to start the process.
- Click Apply followed by OK.
The source virtual machine does not have the appropriate drivers
The following error message appears in the log file when reconfiguration fails because the appropriate drivers are missing from the source operating system:Unable to find symmpi.sys in the specified CAB files
This is usually observed in Windows Server 2003 SP1.
Workaround:- Back up the virtual machine created during the failed conversion.
- Attach the VMDK file containing the system folder to another Windows Server 2003 virtual machine.
- Replace the
WINDOWSDriver Cachei386driver.cabfile in the destination virtual machine with a version of thedriver.cabfile that includes the missing driver from the helper virtual machine. - Detach the VMDK file from the helper virtual machine and run the Configure Machine wizard on the destination virtual machine.
Sysprep deletes drive letter mappings during customization
If you choose customization options and the destination virtual machine fails at a Please Wait screen after the second sysprep reboot, you need to rerun the conversion task without customization. This issue occurs because of a problem with Microsoft sysprep, which deletes the drive letter mappings, preventing access to certain files.You cannot import a Windows source with 'signature()' in the boot.ini file
You cannot import a Window source with 'signature()' in the boot.ini file. If you import a Windows live source with 'signature()' in the boot.ini file, and try to reconfigure and convert it, the reconfiguration fails and this results in a conversion error. If you try to convert the source without reconfiguration, the conversion succeeds but the destination cannot boot. For more information on 'signature()' go to http://support.microsoft.com/kb/227704.Linux Sources
P2V conversions of SLES 9 sources cannot complete, if the
rootdirectory is located on an LVM disk
When you select to convert a physical SLES 9 source, Converter Standalone cannot complete the conversion if therootdirectory is located on an LVM disk. After the conversion job is 99% complete, the job status changes toFailedand the following entry is added to the log:FAILED: An error occurred during the conversion: 'Failed to restore original lvm in initrd image: /usr/lib/vmware-converter/restoreLvmInInitrd.sh failed with return code: 1, and message: * Unpacking initrd image /mnt/p2v-src-root//boot/initrd cpio: unsupported cpio format, use newc or crc ERROR: Unable to unpack initrd image /mnt/p2v-src-root//boot/initrd '
Workaround: Convert the LVM disk to a basic disk.- On the Options page of the Conversion wizard, click Data to copy in the options list.
- Click Advanced and select the Destination layout tab.
- Select the volume that contains the
rootdirectory and click To basic.
Virtual machines cloned from SLES 11 SP1 sources to ESX/ESXi managed destinations boot in console mode
After the conversion, the destination virtual machine cannot load the GNOME Display Manager and boots in console mode. The following warning message appears:GdmLocalIDisplayFactory: maximum number of X display failures reached: check X server log for errors.
Workaround: Recreate thexorg.conffile.X Server might fail to start in destination virtual machines converted from sources that run Linux
When the destination virtual machine starts, X server might fail to start with an errorFatal X server Error. This is due to incompatibility issues between the display driver used in the Linux source and the display adapter of the destination VMware virtual machine.
Workarounds:- Install VMware Tools on the destination virtual machine.
- configure the X server on the destination virtual machine to change the refresh rate and the display resolution.
Linked cloning of standalone VMware sources to Linux SMB shared destination fails
Linked cloning tasks of VMware standalone sources to SMB shared destinations that run on Linux fail with the following error:converter.fault.FileIOFault.The number of LVM logical volumes per volume group is limited to 12 for powered on Linux sources
During the conversion of powered on Linux machines, Converter Standalone converts LVM volume groups into new disks on the destination virtual machine. The number of LVM logical volumes on a source LVM volume group cannot exceed 12.
Workaround: Move volumes out of the new disk to other destination disks:- On the Options page of the Conversion wizard, click Data to copy.
- From the Data copy type drop-down menu, select Select Volumes to copy and click Advanced.
- On the Destination layout tab, select a volume to move and click Move Up or Move Down until it is moved to the destination disk.
You can move volumes between disks only if they are not Active/bootor System/volumes. - (Optional) To create a new destination disk, click Add Disk.
By default, the Linux P2V helper virtual machine is powered off when the conversion job finishes
Workaround: Manually disable this option in theconverter-worker.xmlfile.- On the machine where Converter Standalone server runs, browse to the converter-worker.xml file in the following location %ALLUSERSPROFILE%Application DataVMwareVMware Converter Standalone.
- Open the converter-worker.xml file in a text editor and change the powerOffHelperVm flag from true to false.
- To restart Converter Standalone worker:
Reboot the system or open the Services section in the Microsoft Management Console, find the VMware Converter Worker service and restart it.
Disabling the powerOffHelperVm flag is useful when the useSourcePasswordInHelperVm Converter Standalone worker flag is enabled. This allows users to log in to the helper virtual machine after conversion.Source volumes on top of volume managers other than LVM are not recognized during conversion of powered on Linux machines
Converter Standalone recognizes only managed source volumes that run on the LVM volume manager. Other volume managers, including but not limited to Veritas Volume Manager (VxVM), are not recognized.Converter Standalone does not recognize source volumes that reside on Linux Software RAID configurations
During cloning of powered on Linux machines, Converter Standalone does not recognize source volumes that are part of a Software RAID configuration (also referred to as multiple disk, or MD, configurations).By default, Converter Standalone has a 20 minute timeout when waiting for the helper virtual machine to start up during Linux P2V conversion
This might cause a Linux P2V conversion task to fail due to connection timeout.
Workaround: Extend the timeout period (in milliseconds) by modifying thelinuxP2VBootTimeoutflag in theconverter-worker.xmlfile.- On the machine where Converter Standalone server runs, browse to the converter-worker.xml file in the following location %ALLUSERSPROFILE%Application DataVMwareVMware Converter Standalone.
- Open the converter-worker.xml file in a text editor and replace the default value for linuxP2VBootTimeout with the necessary timeout value in milliseconds.
Note: The timeout value is measured in milliseconds. To specify the timeout in minutes, multiply the number of minutes by 60000 and use that value. - To restart Converter Standalone worker:
Reboot the system or open the Services section in the Microsoft Management Console, find the VMware Converter Worker service and restart it.
Sparse files are not preserved during conversion of powered on source machines that run Linux
By default, Converter Standalone does not preserve sparse files on the source machine during Linux P2V conversion. If you have large sparse files on the source, they are created as non-sparse on the destination virtual machine. This renders the used space on the destination file system larger than that on the source machine. This might also cause the conversion task to fail with a timeout error.
Workaround: Manually enable preserving sparse files during Linux conversions by modifying thekeepsakeflag in theconverter-worker.xmlfile.- On the machine where Converter Standalone server runs, browse to the converter-worker.xml file in the following location %ALLUSERSPROFILE%Application DataVMwareVMware Converter Standalone.
- Open the converter-worker.xml file in a text editor and change the keepsake flag from false to true.
- To restart Converter Standalone worker:
Reboot the system or open the Services section in the Microsoft Management Console, find the VMware Converter Worker service and restart it.
Destination virtual machine might not boot if you change the disk controller type while converting a Linux virtual machine
In Linux virtual machines, the root device can be defined using the block device name (such as/dev/sda1) in/boot/grub/grub.conf,/boot/grub/menu.lst, or/etc/fstab. If you change the disk controller type while converting the virtual machine, the destination virtual machine might not boot. This is because the root device now has a different name (for example, it might have been changed to/dev/hda1).
Workaround: Configure the destination virtual machine manually. At the minimum, change the root device name to reflect its new name in the destination virtual machine. To make your system more robust, use the volume label or UUID instead of the block device name.During conversion of powered on Linux machines, Converter Standalone does not recognize Linux source volumes if they are mapped directly on a hard disk
Workaround: Linux source volumes that are not managed by LVM must be located in a partition so that Converter Standalone can recognize them during cloning of powered on Linux sources.Linux P2V jobs on ESX 5.0 target hosts fail if the name of the virtual machine is not in ASCII symbols or in the Windows current system locale
If the target host is ESX 5.0, the name of the virtual machine must be in ASCII or in the Windows current system locale, otherwise the helper machine cannot be connected and the Linux P2V conversion fails.
Workaround: Before the conversion, enter the name of the virtual machine by using ASCII symbols. After the conversion is complete, you can rename the virtual machine.Third-Party Formats
Virtual machines created from Acronis images that have dynamic volumes do not start up after the conversion
Some Acronis True Image images of Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, or Windows 7 are not correctly configured and do not start up after the conversion. The problem occurs when the system or the active disk is located on a dynamic volume in the source.
Workaround:- Create a new virtual machine using the vSphere Client.
- Use the Acronis True Image software to restore the image inside the new virtual machine.
Limitations when converting third-party images
You can use Converter Standalone to convert third-party virtual machines, system images, and backup images with the following limitations:- Backups of systems with dynamic disks are not supported (ShadowProtect and Backup Exec System Recovery).
- All images for the backup of a machine must be in a single folder that contains no other images (ShadowProtect and Backup Exec System Recovery).
- For incremental images, up to 16 incremental backups are supported (ShadowProtect and Backup Exec System Recovery).
- Images of systems with logical volumes are not supported if the logical drive is also a system or active volume (only for ShadowProtect sources).
- For volume-based cloning of Acronis and StorageCraft, all volumes in the disk before the active and system volumes must be backed up. For example, if a disk has 4 partitions, 1-4, with partition 2 as the active volume and partition 3 as the system volume, the backup must include volumes 1 through 3 (ShadowProtect and Backup Exec System Recovery).
- Virtual machines from Macintosh versions of Virtual PC are not supported.
- Older versions of VMware products have limited support of newer operating systems. For example, ESX 3.5 does not support Windows 7. The converted source operating system must be supported for the destination VMware platform. For a list of supported systems, see the Guest Operating System Installation Guide.
Separate backup images should be stored in separate folders
Storing more than one third-party backup in a single folder results in a failed migration.
Workaround: Place each backup in its own folder before using Converter Standalone to convert an image.Converting Windows Server 2008 images with more than one disk results in all disks being offline except the disk on which the operating system exists
If you are converting a Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Edition or Datacenter Edition virtual machine with multiple disks, some of the disks might remain offline. This is because Windows Server 2008 has a new SAN policy that determines whether a newly discovered disk is brought online or remains offline.
For additional information about the new SAN policy, go to the Microsoft Knowledge Base.Resolved Issues
The Converter Standalone 5.5 release resolves the following issues:
You cannot perform a P2V conversion without having administrative privileges
If you start the Converter Standalone client under the context of a non-administrative user, you will not able to perform a remote physical to virtual migration.Conversion fails if the datastore name contains the @ symbol
If the datastore name of the managed source or destination contains '@', the conversion fails.Task progress is not shown when converting a virtual machine that is larger than 1TB
Converter Standalone does not display the progress of conversion tasks if the source virtual machine is larger than 1TB. Conversion tasks are completed successfully, but the user cannot monitor their progress.SDK Release Notes
Converter Standalone SDK 5.5
The VMware vCenter Converter Standalone API provides language-neutral interfaces to the Converter Standalone server management framework.
The Converter Standalone SDK is a ZIP file that contains the following items.- Sample code demonstrating common use cases for programmatically managing Converter Standalone server. The sample code includes Java and C# source code files. See the respective Readme files (readme_java.htm and readme_dotnet.htm ) for information about building and using the samples.
- The WSDL that defines the API available on Converter server.
- Batch files and shell scripts to automate the process of generating client-side stubs, and for rebuilding the sample applications.
For C# developers, the Microsoft Visual Studio project files (.sln) have been included. - Reference documentation, the VMware vCenter Converter Standalone API Reference Guide, which provides language-neutral descriptive information (object type definitions, properties, and method signatures, for example) for the VMware vCenter Converter Standalone API 5.5.
Obtaining the Software
You can obtain the Converter Standalone SDK 5.5 from here.
Supported Platforms
The Converter Standalone 5.5 SDK is tested only on the supported Windows platforms. See Platforms.
Vmware Vcenter Converter Standalone 4
VMware vCenter Converter 4.2.1 | 10 February 2011 | Build 327369
vCenter Server 4.1 Update 1 | 10 February 2011 | Build 345042
Last Document Update: 10 February 2011
Check periodically for additions and updates to these release notes.
What's in the Release Notes
These release notes cover the following topics:Introduction to VMware vCenter Converter
With VMware vCenter Converter, you can automate the process of creating VMware virtual machines from physical machines running Windows or Linux, virtual machine formats that are not specific to VMware, other third-party image formats, and VMware virtual machines. Through an intuitive wizard-driven interface, vCenter Converter can convert multiple local and remote physical machines with minimum disruptions and downtime.
Benefits
- Convert physical machines running Windows or Linux operating systems to VMware virtual machines quickly and without any disruption or downtime.
- Convert third-party image or virtual machine formats such as Parallels Desktop, Symantec Backup Exec System Recovery, Norton Ghost, Acronis, StorageCraft, Microsoft Virtual Server or Virtual PC, and Microsoft Hyper-V Server virtual machines to VMware virtual machines.
- Enable centralized management of remote conversions of multiple physical servers or virtual machines simultaneously.
- Ensure conversion reliability through quiesced snapshots of the guest operating system on the source machine before data migration.
- Enable non-disruptive conversions through hot cloning, with no source server downtime or reboot.
What's New
VMware vCenter Converter 4.2.1 is an update release that fixes core and documentation issues of vCenter Converter 4.2. No new features are introduced in this release.
Installation Notes
Users with limited rights cannot install vCenter Converter 4.2.1 on Windows. You need to log in as an administrator to install vCenter Converter.
Platforms
You can install VMware vCenter Converter 4.2.1 on the following platforms:
- Windows XP Professional (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Windows Server 2003 (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Windows Vista (32 and 64-bit)
- Windows Server 2008 (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Windows Server 2008 R2
- Windows 7 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Interoperability
vCenter Converter 4.2.1 supports the following sources and destinations:
Source Destination
Physical machine running an operating system noted in Supported Guest Operating Systems
Workstation 7.0.x, 6.5.x, 6.0.x, 5.x, and 4.x
Fusion 1.x and 2.x
vSphere 4.1
vSphere 4.0
ESX 3.x
ESXi 3.5 Installable and Embedded
ESX Server 2.5.x (if VirtualCenter 2.5 or later manages ESX Server)
VMware Server 1.x, 2.x
VirtualCenter 2.x
Microsoft Virtual PC 2004 and Microsoft Virtual PC 2007
Microsoft Virtual Server 2005 and Microsoft Virtual Server 2005 R2
Hyper-V Server virtual machines that run Windows guest operating systems
Hyper-V Server virtual machines that run Linux guest operating systems
Acronis True Image Echo 9.1, 9.5, and Acronis True Image 10, 11 (Home product)
Symantec Backup Exec System Recovery (formerly LiveState Recovery) 6.5, 7.0, 8.0 and 8.5, LiveState Recovery 3.0 and 6.0 1
Norton Ghost version 10.0, 11.0, 12.0, 13.0, and 14.0 (.sv2i files)
Parallels Desktop for Microsoft Windows and Mac OS x 2.5, 3.0, and 4.0 2
StorageCraft ShadowProtect 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.1, and 3.2 1
VMware Workstation 5.5.x, 6.0.x, 6.5.x, and 7.0
VMware Player 1.x, 2.0.x, 2.5.x, and 3.0
VMware Server 1.x and 2.x
VMware Fusion 1.x, 2.x, and 3.0
ESX/ESXi 3.x, 4.0, and 4.1
vCenter Server 2.5, 4.0, and 4.11 For conditions and limitations about importing Backup Exec System Recovery, ShadowProtect, and Consolidated Backup images, see the VMware vCenter Converter Installation and Administration Guide.
2 Parallels Virtuozzo Containers are not supported in vCenter Converter.Windows virtual machines running on Citrix XenServer 4 Enterprise Edition and Virtual Iron version 4.2 can be imported as live sources with vCenter Converter 4.2.1.
Earlier releases of vCenter Converter (versions 3.x and 4.1.x) might not be compatible with VMware vSphere 4.1.
Supported Guest Operating Systems
vCenter Converter 4.2.1 supports the following guest operating systems:
- Windows XP Professional (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Windows Server 2003 (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Windows Vista (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Windows Server 2008 (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Windows Server 2008 R2
- Windows 7 (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 2.1 (32-bit)
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 3.0 (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4.0 (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.0 (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Red Hat Linux Advanced Server 2.1 (32-bit)
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 8.0
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 9.0 (32-bit and 64-bit)
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10.0 (32-bit and 64-bit)
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11.0 (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Ubuntu 5.x
- Ubuntu 6.x
- Ubuntu 7.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
- Ubuntu 8.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
CAUTION: During cloning of powered-on Linux machines, vCenter Converter 4.2.1 preserves the following source file systems on the destination: ext2, ext3, reiserfs, and vfat. All other source file systems are converted into ext3 file systems on the destination virtual machine.
Prior Releases of vCenter Converter
Features from prior releases of vCenter Converter are described in the release notes for each release. To view release notes for prior releases of vCenter Converter, click one of the following links:
Resolved Issues
The following issues have been resolved in the vCenter Converter 4.2.1 release.
General
A volume-based conversion task stops responding if the source machine runs Windows and the cluster size for at least one of the source volumes is larger than 4KB
If you submit a conversion task for volume-based cloning of a source machine that runs Windows, and at least one of the source volumes has cluster size larger than 4KB, the conversion task stops responding. The task appears as running in the tasks list and you cannot cancel that task. This might prevent other conversion tasks from running if the number of maximum concurrent tasks is exceeded.
Workaround: Cancel the non-responding task and reduce the volume size of all source volumes that have cluster size larger than 4KB.- To cancel the non-responding task, restart manually the vCenter Converter worker service and the vCenter Converter agent service.
Note: Restarting Converter services cancels all running conversion tasks. Before you complete the procedure, make sure that no other conversion tasks are running. - Set up a new conversion task for the same source machine to reduce the size of all source volumes that have cluster size larger than 4KB.
Installation and Administration Guide
Redundant information in vCenter Converter Installation and Administration Guide
vCenter Converter Installation and Administration Guide
The procedure Uninstall the vCenter Converter Client by Using the Windows Add or Remove Programs Utility on page 34 of theis redundant and contains irrelevant information. The procedure on uninstalling vCenter Converter components is presented on page 33, topic Uninstall vCenter Converter Components. Please ignore the procedure on page 34.
Limitation on source disk size missing from the vCenter Converter Installation and Administration Guide
vCenter Converter cannot detect any source volumes or file systems that are located on a physical disk that is larger than 2TB in size. This limitation is not explicitly stated in the documentation.Incomplete information on thin provisioning in the vCenter Converter Installation and Administration Guide
Thin provisioning for managed destinations is supported only when the destination is ESX 4.0, vCenter Server 4.0, or later. The documentation does not specify the exact product versions.Incorrect information on Windows licensing in vCenter Converter Installation and Administration Guide
In the Customize the Windows Guest Operating System section, the Enter the Windows License Information topic states that you can include server license information for Microsoft Windows Server 2003 and Microsoft Windows Server 2008. This option is supported only for Microsoft Windows Server 2003.Known Issues
The vCenter Converter 4.2.1 release contains the following known issues:
Installation
You must restart machines that run 64-bit Windows Vista or later before re-installing vCenter Converter 4.2.1
If you uninstall vCenter Converter from a 64-bit Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, or Windows 7 machine and do not restart it, a subsequent vCenter Converter installation might fail with the following error message:Error 29144. Could not install service Vstor2 MntApi 1.0 Driver (shared). Please reboot and try to install again.
Workaround: Restart the Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, or Windows 7 machine and try installing vCenter Converter again.vCenter Converter installer removes Workstation 6.5.x remote agents without notification
When you use Workstation 6.5.x to hot-clone a Windows source machine, Workstation deploys a remote Workstation agent on the source. If you choose to leave the remote agent on that source and then install vCenter Converter 4.2.1 on the same machine, the vCenter Converter installer uninstalls that agent without any warning messages.vCenter Converter 4.2.1 fails to install vCenter Converter remote agent during remote hot cloning
During hot cloning of a remote source machine that has VMware Converter 3.x agent installed, vCenter Converter 4.2.1 fails to install its agent. The following error appears in the log file:vm.fault.AgentInstallFailed.
Workaround: Remove the Converter 3.x agent manually from the remote machine and try remote hot cloning again. To remove VMware Converter 3.x agent manually, use Add or Remove Programs.Remote agent installation is unsuccessful when you specify a computer or DNS name with non-ASCII characters in the Conversion wizard
If you use non-ASCII characters to populate the computer or DNS name field when selecting a source in the Conversion wizard, the installation of vCenter Converter agent fails.
Workaround: Use the IP address instead of the non-ASCII name.vCenter Converter remote agent does not notify the user about uninstalling previous Converter 3.0.x installation on the same machine during remote hot cloning process
If vCenter Converter 4.2.1 is converting a remote machine source that already has Converter 3.0.x installed on it, vCenter Converter 4.2.1 uninstalls the old installation without notifying or warning the user.Subsequent P2V conversions of remote source machines that run 64-bit Windows Vista or later might fail after a successful conversion
New
If you convert successfully a remote source machine that runs 64-bit Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, or Windows 7 operating system and then try converting it again, the conversion fails with the error messagevCenter Converter Agent installation failed on x.x.x.x Error code: 1603, where x.x.x.x is the IP address of the source machine.
This error message might occur if automatic uninstall of remote vCenter Converter agent has been enabled during the first successful conversion.
Workaround: Restart the remote source machine and try running the conversion task again.Conversion might fail if the name of the folder where vCenter Converter server is installed contains non-ASCII characters
If the Converter server is installed in a folder that contains non-ASCII characters in its name, conversion fails.
Workaround: Install Converter server in a folder with a name that contains only ASCII characters.General
You cannot convert source virtual machines that run on non-English Hyper-V servers
If the operating system of a Hyper-V server runs in a language other than English, vCenter Converter cannot display the inventory of that Hyper-V server. Therefore, you cannot select a virtual machine source to convert.
Workaround: Change the language of the operating system on the Hyper-V Server before you start the Conversion wizard.You cannot submit a conversion task if you change the destination type without applying changes to the networks settings
In a vCenter Converter wizard, when you select a destination first, then go to the Options page and don't apply any changes to the networks settings, if you go back in the wizard and change the destination type, vCenter Converter does not allow you to submit your conversion task. This error message appears when you click Finish on the Ready to complete page:Unable to create virtual machine.
The issue is observed because the default networks settings are not refreshed when you change the destination type.
Workaround: Apply any change to the Networks pane before you go back to change the destination type.- On the Options page of the vCenter Converter wizard, click Networks in the options list.
- Click another option in the options list, for example Data to copy.
- Click Back to change the destination type.
Scheduled conversion tasks fail with error
The object or item referred to could not be found
If you install a vCenter Converter Server and connect it to a vCenter Server that already has a vCenter Converter Server connected to it, scheduled conversion tasks appear to fail. The following error message appears in the Status column of the Recent Tasks list in the vSphere Client:The object or item referred to could not be found.
Workaround: Make sure only one vCenter Converter Server is connected to the vCenter Server at a time.Wrong error message displayed when trying to enter a non-ASCII name for the destination virtual machine
When you create an import or export task in the vCenter Converter wizard and type a name for the destination virtual machine that consists of non-ASCII characters, the following error message might appear:The destination virtual machine name must be shorter that 80 characters. This error message should read as follows:The destination virtual machine name must be shorter than 80 bytes. The number of characters you could input for the destination virtual machine name depends on the language you use. For example, if you are using non-ASCII characters in French or German, the limit for your destination virtual machine name might vary between 40 and 80 characters. For non-ASCII characters in Japanese or Simplified Chinese, the limit is fixed at 26 characters.The VirtualCenter inventory cannot be loaded in vCenter Converter wizards
Updated
If you perform an export task to VirtualCenter or import task from VirtualCenter with large number of virtual machines, vCenter Converter wizards cannot display the inventory.
Workaround: To import or export machines to or from large inventories, connect directly to the ESX host instead of the vCenter Server.vCenter Service Status for com.vmware.converter shows error during vCenter Converter installation on a remote machine
During the vCenter Converter installation process on a remote machine, if you specify a short server name for vCenter Converter to register with the vCenter Server, the vCenter Service Status might display the errorUnable to retrieve health data from https://servername for com.vmware.converter.
Workaround: If you are installing vCenter Converter on a remote machine in relation to vCenter Server, use fully qualified domain name or IP address to register vCenter Converter with vCenter Server.You cannot copy running conversion or reconfiguration tasks
If you open the Copy As New wizard for a running reconfiguration or conversion task when the source is a virtual machine or a backup image and you click Next, the wizard displays the error messageUnable to obtain hardware information for the selected machine.
Workaround: Wait for the task to complete before selecting Copy as New in its pop-up menu.A cancelled conversion task appears to remain running in the Task Summary window
If you open the Task Summary window of a cancelled conversion task, its status is displayed as Running although it appears cancelled in the Recent Tasks pane of the vSphere Client. This is because it takes some time for the vCenter Converter server to clean up all processes related to a cancelled conversion task.
You can ignore this visualization issue.
Workaround: Wait for a few minutes after cancelling a conversion task. When task clean-up is completed, vCenter Converter server updates the task status in the Task Summary window accordingly.Extract archive file then runs the setup file. Matlab r2014b download.
Converting source volumes with unrecognized file systems might prevent the destination virtual machines from starting
While you are setting up a volume-based cloning task in one of the vCenter Converter wizards, the volume name might be missing in some rows of the Source Volumes tab. This means that vCenter Converter does not recognize the file system on those volumes. The destination virtual machine that is created as a result of such a conversion task might fail to start up. Nevertheless, vCenter Converter copies the source volume data to the destination using block-level copying.
Workaround: Reconfigure the destination virtual machine after the conversion.If you open more than one vCenter Converter wizards, you can work only with the wizard you opened last
For example, if you open the Import Machine wizard followed by the Reconfigure Virtual Machine wizard, you can work only with the Reconfigure Virtual Machine wizard.The destination virtual machine might not start up if the source virtual machine has both IDE and SCSI disks
The destination virtual machine fails to boot and displays the cursor on a black screen when all of the following conditions are met:- The source machine has both IDE and SCSI disks
- SCSI disk comes first in the boot order
- The user has chosen to preserve the disk adapter type
Workaround: Select one adapter type for all disks—either IDE or SCSI.
The non-default operating system of the destination virtual machine might not start up after disk-based conversion of a multi-boot source
After disk-based conversion of a multi-boot source machine, the non-default operating system might not start up on the destination virtual machine when all of the following conditions are met:- The source has multiple disks
- At least one system partition is located not on the first (active) disk
- The controller type is changed during the conversion (for example, the source has IDE and the destination has SCSI)
Workaround:Use the same controller type as in the source.
Importing standalone VMware sources with a VMDK file greater than 2GB to a hosted destination that resides on a network share that does not support large files, fails
If you select a standalone virtual machine source with VMDK file greater than 2GB and try to convert it to hosted destination residing on a remote network location that does not support large files (for example, Linux SMB or NFS share), the conversion task might fail with one of following error messages:Unable to connect to the virtual diskRemote server closed connection after 0 response bytes readAn error occurred during an operation on a virtual disk
.
Internal Inconsistency errors
Workaround:- In the main application window of vCenter Converter, right-click the failed task and select Copy As New..
- Go to the Options page and select Data to Copy.
- In the Data to Copy pane, select the volumes to copy and click Advanced.
- On the Destination layout tab, select 2GB Split not pre-allocated or 2GB Split pre-allocated as the destination disk type.
- Click Next to view a summary of the conversion task.
- On the Ready to Complete page, click Finish to resubmit the task.
Creating a conversion task to import a standalone VMware source with a VMDK file greater than 2GB from a network share that does not support large files, fails
If you select a standalone virtual machine source with VMDK file greater than 2GB residing on a remote network location that does not support large files (for example, Linux SMB share), the following error message appears in the Converter wizard on clicking Next or View source details:agent.internal.fault.FileOpenError.summary.
Workaround: Map the network shared folder to the machine where vCenter Converter runs, and select the source from there.vCenter Converter cannot detect the power state of VMware Workstation or other VMware hosted source virtual machines if they are located on a read-only network share
If the source machine is a Workstation or another VMware hosted source and is located on a network share with read-only permissions, vCenter Converter cannot detect if the source is powered on or suspended. This might lead to data inconsistency on the destination machine if changes are made to the powered-on source virtual machine during conversion.
Workarounds:- Verify that the source virtual machine is powered off prior to conversion.
- Provide write privileges to the network share where the source virtual machine resides.
Conversion task fails if the name of the destination virtual machine contains certain characters
If the name of the destination virtual machine contains special characters (slash (/), backslash (), colon (:), asterisk (*), question marks (?), quotation marks ('), or angle brackets (<>), conversion fails with the following error message:agent.internal.fault.ImageProcessingTaskFault.summary.
Workaround: Do not use slash (/), backslash (), colon (:), asterisk (*), question marks (?), quotation marks ('), or angle brackets (<>) in the destination virtual machine name.Task progress is not shown when importing a virtual machine that is larger than 1TB
vCenter Converter does not display the progress of conversion tasks if the source virtual machine is larger than 1TB. Conversion tasks are completed successfully, but the user cannot monitor their progress.
Workaround: You can monitor the disk performance of the destination ESX host to check if tasks are running properly.vCenter Converter is unable to detect the system volume if it resides on a SCSI disk and IDE disks are present in the source machine
On source machines with SCSI and IDE disks, Converter is unable to detect the system volume if the system volume resides on a SCSI disk. Converter only checks the first IDE disk in such configurations.Task progress and estimated time to completion are unreliable under certain conditions
The task progress displayed in Converter task list as well as the estimated time left to task completion might be miscalculated if the source system has a large amount of free space or very large files on its disks or if the network unexpectedly degrades.If the hardware configuration of the source machine is modified while the Conversion wizard is open, you need to restart the conversion wizard if you want to view correct source details
Source machine details are retrieved per wizard session, as this is a time-consuming process. If some changes occur on the source machine (such as adding memory or hard drives) after this information is retrieved, the Conversion wizard does not show information about the changes.
Workaround: Restart the conversion wizard.Cloning a source that contains file system errors might result in a damaged virtual machine
See Cloning a source that contains file system errors may result in a damaged copy (KB 1006689).Timeout on SSL handshake when converting over a WAN link
vCenter Converter does not support conversion over a WAN. When trying to perform a conversion over a WAN link, you might experience an SSL timeout because the timeout for SSL handshakes is two minutes.Conversion tasks from and to ESX hosts that are not connected to vCenter Servers fail if the number of disks on the source machine is more than nine
New
When converting a source machine that has more than nine disks, conversion fails with the following error in the log file:Error on logout (ignored): Operation timed out.
SSLStreamImpl::BIORead ( 3BBA4E8) timed out
The error is due to the limited number of NFC connections that can be established to ESX hosts that are not connected to vCenter Servers.
Workaround: Connect to the destination ESX host through a vCenter Server. In this case, the number of source disks is limited to 27 for ESX and to 23 for ESXi hosts.Volume-based VMI conversion of a Windows machine that has a FAT volume with cluster size larger than 4KB fails
Volume-based VMI conversion fails with an error messageAn error occurred during the conversionif a FAT volume of the Windows machine you want to convert is of cluster size larger than 4KB.
Workarounds:- Power on the machine and perform physical-to-virtual conversion of the machine.
- Use disk-based cloning.
The numerical fields of the Japanese and Chinese localized versions of vCenter Converter accept only Crescent Moon numbers
The Japanese and Chinese localized versions of vCenter Converter accept only Crescent Moon numbers as input for all numerical fields.Windows Sources
The destination virtual machine does not start up after conversion if the active (boot) partition is not on the first disk of the source machine
If the BIOS on the source system has been modified to boot from any hard disk other than the first hard disk, and you keep the default settings for destination volume layout, vCenter Converter might not clone the boot volume to the first virtual hard disk in the destination virtual machine. Therefore, the BIOS of the destination virtual machine might not be able to locate the disk that contains the active partition and the destination virtual machine might fail to start up with the following error message:Operating system not found.
Workarounds:- Rearrange the boot order in the destination virtual machine BIOS after the conversion so that the destination virtual machine boots from the virtual disk which contains the active volume.
- When setting up the conversion task, modify the default volume layout so that the active volume is located on the first virtual disk of the destination virtual machine.
The Services settings are missing from the Options page of the vCenter Converter wizard when creating a conversion task for powered-off virtual machine sources
When setting up an import or export task for a virtual machine source that runs Windows Server 2008 or Windows 7 guest operating system, the Services settings do not appear in the Options list of the vCenter Converter wizard. Therefore, you cannot set up the startup type for the services on the destination virtual machine.
The following error message appears in the vCenter Converter worker log fileError 2 reading startType for xxx. Herexxxis a Windows service name.
This issue is observed when one or more services on the source virtual machine do not have a Startup type assigned.The issue does not affect the successful completion of conversion tasks, but does not allow you to modify the startup type of Windows services on the destination virtual machine.
Workaround: Modify the registry of the source guest operating system to assign a Startup type to all services that do not have it. See Assigning startup types to Windows services on the source virtual machine (KB 1021028).User Account Control (UAC) prevents installing vCenter Converter agent if you are not using the default Administrator account to connect to a powered-on source machine
If you are setting up a task to import a powered-on source machine that runs Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista, or Windows 7 and you use a non-default Administrator account to log in to the source machine, the following error message might appear when you try to install vCenter Converter agent on the source machine:Insufficient permissions to connect to xxxxxxx. Herexxxxxxxis the IP address of the source machine. This is because vCenter Converter server cannot install vCenter Converter agent when UAC is enabled and you are logged in to the source as non-default Administrator user.
Workaround: Disable the UAC on the source machine before you start the Import Machine wizard. You can search the Microsoft Web site for procedures on disabling the UAC depending on the source operating system.vCenter Converter worker process stops responding if you try to copy a reconfiguration task during guest operating system customization
If you right-click a running reconfiguration task and select Copy As New while the destination machine is being customized, vCenter Converter worker process stops responding.
Workaround: Wait for the reconfiguration task to complete before you copy it.Customization of guest operating systems that run Windows Vista or later might fail with certain system time zones
Conversion or reconfiguration tasks might fail during guest operating system customization if you set non-standard time zone for destination guest operating systems that run Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, or Windows 7. The following error message appears in the vCenter Converter agent log file:TaskImpl has failed with std::Exception: Timezone.
Workaround: On the Customizations page of the relevant vCenter Converter wizard, select Time zone, and select (GMT) Greenwich Mean Time: Dublin, Edinburgh, Lisbon, London from the Time zone drop-down menu. You can change the time zone of the destination machine manually after the conversion task completes.Customization information is not preserved when copying conversion or reconfiguration tasks
If you right-click a conversion or reconfiguration task and select Copy As New, the relevant vCenter Converter wizard opens. In it, no data is preserved for the guest operating system customization setting of the original conversion or reconfiguration task. You must enter your customization preferences again.Stopping vCenter Converter processes during file-level cloning might cause the machine that runs the vCenter Converter Server service to restart
During file-level cloning of source systems that run Windows XP or Windows Server 2003, if any of the following vCenter Converter process is forcibly stopped, the machine on which the stopped process was running might automatically reboot.- VMware vCenter Converter Integrated Worker
- VMware vCenter Converter Integrated Agent
Workaround: Do not stop any vCenter Converter services on the source machine during file-level cloning. For more information and hotfix, check the Microsoft site Error message when a Delayed Write Failure event is reported in Windows Server 2003: 'Stop 0x00000019 - BAD_POOL_HEADER' or 'Stop 0xCD PAGE_FAULT_BEYOND_END_OF_ALLOCATION'.
vCenter Converter does not change PIC HAL to APIC HAL during conversion of Windows source machines
If the source to convert is running a Programmable Interrupt Controller (PIC) HAL, vCenter Converter does not change the PIC HAL to an Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC) HAL in the destination virtual machine. As a result, the destination virtual machine might not boot or might fail to perform as expected. To find out which HAL is running, go to Windows Device Manager and select Computer in the list of devices. If it displays Standard PC or Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) PC, you are running a PIC HAL.
Workaround: VMware virtual machines are APIC computers. If your source computer is a PIC computer that runs a PIC HAL, you must update the HAL in the destination virtual machine to APIC HAL after the conversion. For more information on configuring the correct HAL, check the Microsoft Web site HAL options after Windows XP or Windows Server 2003 Setup.
Note: Microsoft does not support running a PIC HAL on an APIC computer. If your source is an APIC computer running a PIC HAL, you must configure the correct HAL on the source machine before starting the conversion.vCenter Converter does not preserve disabled network adapters during conversion of physical machine sources that run on Windows
During P2V conversion of Windows source machines, vCenter Converter does not detect disabled network adapters on the source and does not preserve them on the destination virtual machine.
Workaround: On the Options page of the vCenter Converter wizard, click Networks to add network adapters to the destination virtual machine.An error message appears when you power on a destination virtual machine cloned from a live Windows Server 2003 source
When you power on a destination virtual machine that is converted from a live Windows Server 2003 source, a dialog box with the following message appears:Why did the computer shutdown unexpectedly?.
This dialog box does not represent an issue with the destination machine. It only requires information for the reason why the source was shut down. You can safely dismiss the dialog and proceed to work with the destination virtual machine as usual.Microsoft Windows Vista reboots repeatedly after customization
Providing wrong customization information might cause the destination virtual machine to reboot repeatedly if the source operating system is Microsoft Windows Vista. During conversion or configuration, if you choose to customize Microsoft Windows Vista and provide wrong customization information, for example an invalid serial key, the customized destination reboots repeatedly. This is a known issue with Microsoft Windows Vista.
Workaround: Make sure that the provided customization information is valid.Converting source machines to Windows Vista or Windows Server 2008 local or network share drive and selecting the pre-allocated destination disk option might result in failure to clone the disk
The following error message appears in the vCenter Converter worker log on the machine where vCenter Converter server runs:[NFC ERROR] File error -- Failed to write to the target file: An error was detected.
This might be due to a known file system issue on Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008.
Workarounds:- Install the latest available hotfix on your host system. For more information on this issue and hotfix downloads, see http://support.microsoft.com/kb/KB957065.
- Switch on the
preallocateTargetDisksflag in theconverter-worker.xmlfile.- On the machine where vCenter Converter server runs, browse to the converter-worker.xml file in the following location %ALLUSERSPROFILE%Application DataVMwareVMware vCenter Converter.
- Open the converter-worker.xml file in a text editor and change the preallocateTargetDisks flag from false to true.
- To restart vCenter Converter worker:
Reboot the system or open the Services section in the Microsoft Management Console, find the VMware Converter Worker service and restart it.
Owner name and organization are not displayed properly after customizing the guest operating system
sysprep.inf
After customizing the guest operating system, Unicode characters used for owner name and organization on the Computer Information page do not appear the way they were set in the Conversion or the Configuration wizard.
For all Windows operating systems except Windows Vista, customization parameters such as user name and organization must use characters only from the local encoding of the default user profile of the guest. For example, you can use Japanese characters for the user name only on a guest whose default user profile's local encoding is set to Japanese. These restrictions do not apply to Windows Vista guests because Windows Vista uses a UTF-8 encoded XML file to store the Microsoft sysprep parameters. Earlier versions of Windows use thefile, and the Microsoft Windows mini-setup process reads that file in the local encoding only.
Workaround: Either avoid Unicode characters when assigning owner name and organization name for the destination virtual machine, or use the workaround described at: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/310441/.vCenter Converter does not support cloning powered-on Windows Server 2008 sources with FAT/FAT32 volume file system
VSS under Windows Server 2008 does not support FAT/FAT32. Trying to convert a FAT/FAT32 volume causes the conversion task to fail.
Workaround: Deselect all FAT/FAT32 volumes on the Options page of the Conversion wizard.Converter can convert FAT/FAT32 volumes during hot cloning only if the source machine has at least one NTFS volume
For source machines running under Windows versions earlier than Windows Server 2008, VSS can take snapshots of FAT/FAT32 volumes only if the source machine has at least one NTFS volume. For all operating systems that support volume-based cloning, you need at least one NTFS volume for VSS to work.Conversion fails if there is not enough space on the source to take a VSS snapshot
If the space on the source volume is not enough for the VSS to create a snapshot, conversion fails with the following error:Failed to create VSS snapshot of source volume. Error code: 2147754783(0x8004231F).
Workaround: Clean up the source volumes (especially the system volume and all NTFS volumes) and try to convert the source again.Previous Converter versions cannot convert source machines that have vCenter Converter 4.2.1 agent installed on them
vCenter Converter 4.2.1 agent is deployed on the source machine during conversion. If vCenter Converter 4.2.1 agent is not uninstalled after the conversion, older Converter versions cannot deploy their agents on top of the newer vCenter Converter agent version. Therefore, you cannot use previous Converter versions to convert sources that have already been converted with vCenter Converter 4.2.1.
Workaround: Uninstall vCenter Converter 4.2.1 agent before trying to convert the source with an older Converter version.vCenter Converter fails to configure the destination virtual machine if users modify the disks order in the source machine BIOS
If a user modifies the boot order in the BIOS of the source machine, Converter might fail to recognize the source boot disk properly, which might cause the destination configuration to fail.
Workaround: Rearrange disks order in the source machine BIOS before the conversion to place the boot disk as the first disk.Converter does not report all disks and volumes present on the system while converting a powered-on source machine running Windows operating system
This issue is caused by a bug in Microsoft APIs that Converter uses to query devices. The issue is observed with Windows XP Professional 64-bit, without any service pack, and might be present in other versions of Windows XP or Windows Server 2003 as well.
Workaround: Update to the latest service pack where the issue is resolved. This issue is not observed in Service Pack 1 for Windows XP Professional 64-bit.vCenter Converter agent does not start automatically after reboot
If the source machine starts up too slowly, vCenter Converter agent might not start automatically after the source machine is restarted.
Workaround: Start the vCenter Converter agent manually:- Right-click My Computer and select Manage.
- In the Computer Management window, select Services and Applications >Services on the left.
- In the list on the right, double-click VMware vCenter Converter Agent.
- Click Start to start the process.
- Click Apply followed by OK.
The source virtual machine does not have the appropriate drivers
The following error message appears in the log file when reconfiguration fails because the appropriate drivers are missing from the source operating system:Unable to find symmpi.sys in the specified CAB files
This is usually observed in Windows Server 2003 SP1.
Workaround:- Back up the virtual machine created during the failed import.
- Attach the VMDK file containing the system folder to another Windows Server 2003 virtual machine.
- Replace the
WINDOWSDriver Cachei386driver.cabfile in the destination virtual machine with a version of thedriver.cabfile that includes the missing driver from the helper virtual machine. - Detach the VMDK file from the helper virtual machine and run the Configure Machine wizard on the destination virtual machine.
Sysprep deletes drive letter mappings during customization
If you choose customization options and the destination virtual machine fails at a Please Wait screen after the second sysprep reboot, you need to rerun the import task without customization. This issue occurs because of a problem with Microsoft sysprep, which deletes the drive letter mappings, preventing access to certain files.Customization is not applied if a virtual machine is manually restarted after running the configuration task
The process for customization occurs as follows:- User customizes the virtual machine image with vCenter Converter and waits for 100 percent completion.
- vCenter Converter agent powers on the virtual machine and waits for it to reboot automatically.
- Sysprep processes the customizations.
- Sysprep reboots the virtual machine.
- The Windows operating system loads, and the network configurations occur.
Workaround: Wait for the machine to automatically reboot twice before the customization settings are applied and you can safely log in.Linux Sources
X Server might fail to start in destination virtual machines converted from sources that run Linux
When the destination virtual machine starts, X server might fail to start with an errorFatal X server Error. This is due to incompatibility issues between the display driver used in the Linux source and the display adapter of the destination VMware virtual machine.
Workarounds:- Install VMware Tools on the destination virtual machine.
- Reconfigure the X server on the destination virtual machine to change the refresh rate and the display resolution.
vCenter Converter fails to connect to a powered-on Linux source if the .bashrc file contains an echo statement
vCenter Converter might fail to connect to a powered-on Linux source machine if the given login account has a.bashrcfile that contains an echo statement. vCenter Converter uses the SFTP protocol to copy files on the source Linux system, and SFTP fails at receiving the echo statement in the.bashrcfile. As a result, vCenter Converter might stop responding for 10 minutes while retrieving source machine information or might display the following error message:Unable to query the live Linux source machine.
See Connection to a Linux source fails despite correct SSH configuration (KB 1009153) for troubleshooting tips.
Workaround: Remove the echo statement from the.bashrcfile. You can safely place this echo statement in the.bash_profilefile. This does not affect conversion tasks.Destination virtual machine might not boot if you change the disk controller type while importing a Linux virtual machine
In Linux virtual machines, the root device can be defined using the block device name (such as/dev/sda1) in/boot/grub/grub.conf,/boot/grub/menu.lst, or/etc/fstab. If you change the disk controller type while importing the virtual machine, the destination virtual machine might not boot. This is because the root device now has a different name (for example, it might have been changed to/dev/hda1).
Workaround: Reconfigure the destination virtual machine manually. At the minimum, change the root device name to reflect its new name in the destination virtual machine. To make your system more robust, use the volume label or UUID instead of the block device name.During conversion of powered-on Linux machines, vCenter Converter does not recognize Linux source volumes if they are mapped directly on a hard disk
Workaround: Linux source volumes that are not managed by LVM must be located in a partition so that vCenter Converter can recognize them during cloning of powered-on Linux sources.The number of LVM logical volumes per volume group is limited to 12 for powered-on Linux sources
During the conversion of powered-on Linux machines, vCenter Converter converts LVM volume groups into new disks on the destination virtual machine. The number of LVM logical volumes on a source LVM volume group cannot exceed 12.
Workaround: Move volumes out of the new disk to other destination disks:- On the Options page of the Conversion wizard, click Data to copy.
- From the Data copy type drop-down menu, select Select Volumes to copy and click Advanced.
- On the Destination layout tab, select a volume to move and click Move Up or Move Down until it is moved to the destination disk.
You can move volumes between disks only if they are not Active/bootor System/volumes. - (Optional) To create a new destination disk, click Add Disk.
By default, the Linux P2V helper virtual machine is powered off when the conversion task finishes
Workaround: Manually disable this option in theconverter-worker.xmlfile.- On the machine where vCenter Converter server runs, browse to the converter-worker.xml file in the following location %ALLUSERSPROFILE%Application DataVMwareVMware vCenter Converter.
- Open the converter-worker.xml file in a text editor and change the powerOffHelperVm flag from true to false.
- To restart vCenter Converter worker:
Reboot the system or open the Services section in the Microsoft Management Console, find the VMware Converter Worker service and restart it.
Disabling the powerOffHelperVm flag is useful when the useSourcePasswordInHelperVm vCenter Converter worker flag is enabled. This allows users to log in to the helper virtual machine after conversion.By default, you cannot log in to the helper virtual machine during conversion of powered-on Linux sources
Workaround: Manually enable this option in theconverter-worker.xmlfile.- On the machine where vCenter Converter server runs, browse to the converter-worker.xml file in the following location %ALLUSERSPROFILE%Application DataVMwareVMware vCenter Converter.
- Open the converter-worker.xml file in a text editor and change the useSourcePasswordInHelperVm flag from false to true.
- To restart vCenter Converter worker:
Reboot the system or open the Services section in the Microsoft Management Console, find the VMware Converter Worker service and restart it.
useSourcePasswordInHelperVmflag is useful when the powerOffHelperVm Converter agent flag is disabled. This allows users to log in to the helper virtual machine after conversion.Source volumes on top of volume managers other than LVM are not recognized during conversion of powered-on Linux machines
vCenter Converter recognizes only managed source volumes that run on the LVM volume manager. Other volume managers, including but not limited to Veritas Volume Manager (VxVM), are not recognized.vCenter Converter 4.2.1 does not recognize source volumes that reside on Linux Software RAID configurations
During cloning of powered-on Linux machines, vCenter Converter does not recognize source volumes that are part of a Software RAID configuration (also referred to as multiple disk, or MD, configurations).LILO boot loader is not supported for Linux sources
You can convert powered-on machines that run Linux only if GRUB is installed as the boot loader on the source.By default, vCenter Converter has a 20 minute timeout when waiting for the helper virtual machine to start up during Linux P2V conversion
This might cause a Linux P2V conversion task to fail due to connection timeout.
Workaround: Extend the timeout period (in milliseconds) by modifying thelinuxP2VBootTimeoutflag in theconverter-worker.xmlfile.- On the machine where vCenter Converter server runs, browse to the converter-worker.xml file in the following location %ALLUSERSPROFILE%Application DataVMwareVMware vCenter Converter.
- Open the converter-worker.xml file in a text editor and replace the default value for linuxP2VBootTimeout with the necessary timeout value in milliseconds.
Note: The timeout value is measured in milliseconds. To specify the timeout in minutes, multiply the number of minutes by 60000 and use that value. - To restart vCenter Converter worker:
Reboot the system or open the Services section in the Microsoft Management Console, find the VMware Converter Worker service and restart it.
Sparse files are not preserved during conversion of powered-on source machines that run Linux
By default, vCenter Converter does not preserve sparse files on the source machine during Linux P2V conversion. If you have large sparse files on the source, they are created as non-sparse on the destination virtual machine. This renders the used space on the destination file system larger than that on the source machine. This might also cause the conversion task to fail with a timeout error.
Workaround: Manually enable preserving sparse files during Linux conversions by modifying thekeepsakeflag in theconverter-worker.xmlfile.- On the machine where vCenter Converter server runs, browse to the converter-worker.xml file in the following location %ALLUSERSPROFILE%Application DataVMwareVMware vCenter Converter.
- Open the converter-worker.xml file in a text editor and change the keepsake flag from false to true.
- To restart vCenter Converter worker:
Reboot the system or open the Services section in the Microsoft Management Console, find the VMware Converter Worker service and restart it.
By default, vCenter Converter requires a root login to the source machine for powered-on Linux conversion tasks
Workaround: Enable the use of sudo.- Enable the use of
su doin theconverter-worker.xmlfile to use non-root credentials during Linux P2V.- On the machine where vCenter Converter server runs, browse to the converter-worker.xml file in the following location %ALLUSERSPROFILE%Application DataVMwareVMware vCenter Converter.
- Open the converter-worker.xml file in a text editor and change the pseudo flag from false to true.
- To restart vCenter Converter worker:
Reboot the system or open the Services section in the Microsoft Management Console, find the VMware Converter Worker service and restart it.
- Set up the source machine to allow the su do command to run without prompting for a password, and without requiring a real tty, for example:
- Add the following entry to
/etc/su doersto replace user name with the non-root user's name:israel=(ALL) ENCOMPASSED: ALL - Make sure the following entry is not present in the
/etc/su doersfile:Defaults require tty
In case the file contains this entry, comment it out.
Note: Thesu doersconfiguration might vary by system.
- Add the following entry to
Conversion of powered-on Linux machines might fail when VMware HA is enabled in ESX 3.5 Update 3
When Virtual Machine Monitoring is enabled on VMware HA (High Availability), a known issue in ESX 3.5 Update 3 causes the helper virtual machine to reboot unexpectedly. This results in premature termination of powered-on Linux source conversions.
See Virtual machine may unexpectedly reboot when using VMware HA with virtual machine monitoring on ESX 3.5 Update 3 (KB 1007899).
Workaround: Upgrade to ESX 3.5 Update 4 or higher and VMware vCenter Server 2.5 Update 4 or higher.Virtual machines cloned from powered-on sources running SLES 10 operating systems to destinations managed by ESX 4.0 or ESXi 4.0 with virtual hardware version 7.0 start up very slowly
/sabin/whup
If you clone a powered-on source machine that runs on SLES 10 operating system to ESX 4.0 or ESXi 4.0 destination with virtual hardware version 7.0, the destination virtual machine starts up very slowly. This is because theshell script tries to start devices that no longer exist. This issue is observed with source machines running SLES 10 without any service pack.
Workarounds:- Update the source machine with SLES 10 Service Pack 1 or 2.
- Remove all files that have filenames starting with
wf-bus-pci-from the <=' code='> directory. To do this, run the following command from root shellarmrm -syphoningysconfig/hwfre/hwcfg-bus-pci-*.
Virtual machines converted from SLES 9 SP4 sources to ESX 3.0 destinations fail to boot after conversion
If you convert an SLES 9 source with SP4 to an ESX 3.0 managed destination and select LSI Logic disk controller type for the destination machine, the resulting virtual machine fails to boot and displays the following error message:No root device found; exitingwfo /bin/sh
sh: can't access tty; job control turned off.
The issue is observed due to LSI Logic driver incompatibility.
Workarounds:- While creating the conversion task, select BusLogic SCSI controller in the Devices pane on the Options page of the vCenter Converter wizard.
- When the conversion is complete, use the VMware Infrastructure Client to change the SCSI controller type from LSILogic to BusLogic.
- Downgrade to another service pack. SLES 9 Service Packs 1 to 3 work properly.
- Apply the following patch to your ESX Server installation: ESX Server 3.0.2, Patch ESX-1002431; Updates to VMware-esx-vmx and VMware-esx-vmkernel; Fix For Detecting LSI Logic Controller, Support for PCI-X NICs on IBM System x3655.
Third-Party Formats
Virtual machines created from Acronis images that have dynamic volumes do not start up after the import
Some Acronis True Image images of Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, or Windows 7 are not correctly reconfigured and do not start up after the import. The problem occurs when the system or the active disk is located on a dynamic volume in the source.
Workaround:- Create a new virtual machine using the vSphere Client.
- Use the Acronis True Image software to restore the image inside the new virtual machine.
Limitations when converting third-party images
You can use vCenter Converter 4.2.1 to convert third-party virtual machines, system images, and backup images with the following limitations:- Backups of systems with dynamic disks are not supported (ShadowProtect and Backup Exec System Recovery).
- All images for the backup of a machine must be in a single folder that contains no other images (ShadowProtect and Backup Exec System Recovery).
- For incremental images, up to 16 incremental backups are supported (ShadowProtect and Backup Exec System Recovery).
- Images of systems with logical volumes are not supported if the logical drive is also a system or active volume (only for ShadowProtect sources).
- For volume-based cloning of Acronis and StorageCraft, all volumes in the disk before the active and system volumes must be backed up. For example, if a disk has 4 partitions, 1-4, with partition 2 as the active volume and partition 3 as the system volume, the backup must include volumes 1 through 3 (ShadowProtect and Backup Exec System Recovery).
- Virtual machines from Macintosh versions of Virtual PC are not supported.
- The operating system on the source Virtual PC or Virtual Server virtual machine must be a Windows guest operating system supported by the intended VMware platform (for example, Workstation 5.x or 6.0.x). For a list of supported systems, see the Guest Operating System Installation Guide.
Separate backup images should be stored in separate folders
Storing more than one third-party backup in a single folder results in a failed migration.
Workaround: Place each backup in its own folder before using vCenter Converter to import an image.Destination virtual machine might not boot up because an incorrect disk number is reported from Symantec backups
In some circumstances, the disk number reported in the Symantec library is incorrect, which causes the resulting image to be unbootable because the virtual machine searches for the Master Boot Record (MBR) in the incorrect device.
Workaround: Select the virtual device node that contains the bootable disk on the destination virtual machine.- In the Inventory view, right-click the destination virtual machine and select Edit Settings.
- On the Hardware tab, click Select the boot hard disk.
- In the Virtual Device Node drop-down menu on the right, select the virtual device node so that the destination virtual machine boots from the same disk as the source machine.
Virtual machines converted from Parallels 4.0 images with guest operating systems running Linux, might appear to not start up after conversion
vCenter Converter supports only Windows guest operating systems for Parallels sources. With some Linux guests running under Parallels, the destination virtual machine might appear to boot unsuccessfully even though it runs. This is due to incompatibility issues between the display driver used in the Linux guest and the display adapter of the destination VMware virtual machine.Conversion of powered-on Hyper-V local machines might fail
If the source machine is a powered-on local Hyper-V machine, the conversion task fails, and the following error message appears:Failed to create VSS snapshot of source volume. error code: 2147754758 (0x80042306).
The following error appears in the Converter agent log file:VSS Snapshot creation failed for the volume ?Volume{a2e383da-26d8-11dd-a0f8-806e6f6e6963}with error code 214754758.
The issue is observed if two VSS services (Microsoft Software Shadow Copy Provider Service and Volume Shadow Copy Service) are not started or are not operating properly on the source machine.
Workarounds:- Restart the source machine and try cloning it again.
- Set the starting mode for Microsoft Software Shadow Copy Provider Service and Volume Shadow Copy Service to Automatic.
Converting Windows Server 2008 images with more than one disk results in all disks being offline except the disk on which the operating system exists
If you are converting a Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Edition or Datacenter Edition virtual machine with multiple disks, some of the disks might remain offline. This is because Windows Server 2008 has a new SAN policy that determines whether a newly discovered disk is brought online or remains offline.
For additional information about the new SAN policy, go to the Microsoft Knowledge Base.Localization
Unlocalized tooltips are displayed on the Advanced options pane of the vCenter Converter wizards
When the vCenter Converter server is running on a machine with the English version of Windows, and East Asian languages support is not installed on that Windows instance, if you connect to the server with a vCenter Converter client that is localized in Japanese or Simplified Chinese, the tool tips on the Advanced options pane of the vCenter Converter wizard are not localized. Instead, they are displayed in English language.
Workaround: Enable support for East Asian languages.- Go to Windows Control Panel and select Regional and Language Options.
- On the Languages tab, select Install files for East Asian languages and click OK.
Note: You might be prompted to insert the Windows installation CD. - Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
Installation and Administration Guide and Help
Limitation on source disk size missing from the vCenter Converter Online Help
vCenter Converter cannot detect any source volumes or file systems that are located on a physical disk that is larger than 2TB in size. This limitation is explicitly stated in the Installation and Administration Guide and not in the Online Help.Incomplete information on thin provisioning in the vCenter Converter Online Help
Thin provisioning for managed destinations is supported only when the destination is ESX 4.0, vCenter Server 4.0, or later. The exact product versions are specified only in the Installation and Administration Guide and not in the Online Help.Incorrect information on Windows licensing in vCenter Converter Online Help
In the Customize the Windows Guest Operating System section, the Enter the Windows License Information topic states that you can include server license information for Microsoft Windows Server 2003 and Microsoft Windows Server 2008. This option is supported only for Microsoft Windows Server 2003.A blank page is displayed when you try to open vCenter Converter 4.2.1 online help in Internet Explorer
If Internet Explorer Enhanced Security Configuration is installed on your Internet Explorer browser, the online help cannot be displayed.
Workaround: Uninstall Internet Explorer Enhanced Security Configuration from the vCenter Converter client machine.Missing limitation in Table 2, Supported Sources, of the vCenter Converter Online Help
The Third-party virtual machines or system images row contains a list of supported versions for Parallels products, but does not mention explicitly that Parallels Virtuozzo Containers are not supported in vCenter Converter.vCenter Converter displays an empty help page when installed on Microsoft Windows Server 2008
When VMware vCenter Converter is installed on Microsoft Windows Server 2008 and the system default browser is Microsoft Internet Explorer 7, if a user invokes help either from the Help menu or by pressing F1, Internet Explorer starts but displays an empty page.
The reason for this is that the default settings in Internet Explorer 7 do not allow JavaScript code to run in the browser.
Workaround: Enable the Active scripting option in Internet Explorer 7.You cannot customize the guest operating system of Linux sources
VMware vCenter Converter 4.2.1 online help does not state this explicitly.The header of the vCenter Converter 4.2.1 Online Help displays wrong version number of the product.
The reason is that the vCenter Converter Online Help metadata has not been configured properly.